Updated on 24. April 2022 from ÁYIO-Q Redaktion
Reading time: approx. 5 minutes
I’m sure most readers are familiar with the old folk wisdom: sour makes merry. It beautifully describes the positive influence of sour tasting foods on our state of mind. Sauerkraut, lemons and vinegar do not have an acidic effect on a healthy body, but belong to the alkaline builders. Foods, on the other hand, which produce acids in the organism, do not themselves taste sour. In the following article you will learn about the effects of an alkaline and an acidic diet on humans and how a disturbed acid-base balance can be balanced.
Can we actually become too acidic?
In the field of naturopathy, nothing is discussed as controversially by scientists as so-called hyperacidity. A person would die if their blood suddenly took on an acidic pH. Therefore, our organism has a sophisticated buffer system that neutralizes excess acids immediately. Consequently, from the point of view of a classically trained biologist or chemist, hyperacidity of the body is impossible. To avoid misunderstandings, we will first explain the topic from the perspective of quantum medicine.
What do acidic and alkalic actually mean?
According to the acid-base theory of the chemists Professor Dr. Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted and Professor Dr. Martin Lowry, acids are chemical compounds that release positively charged hydrogen ions (protons, H+). Bases (alkalis), on the other hand, can absorb protons. For clarification, two examples: Hydrochloric acid (HCl) gives off a proton and dissociates in water (H2O) to H3O+ and Cl-. Caustic soda (NaOH) takes up an H+ ion in aqueous solution to form Na+ and H2O.1
Acids and alkali – Effects on the organism
According to current scientific research, the water in our cells and tissues does not exist as a liquid, but has a highly ordered, liquid crystalline structure. For this reason, Professor Brønsted’s and Professor Lowry’s concept of acids and bases has only limited application in the human body.2
Apparently one of the secrets of life is that higher organisms have several hierarchical systems at their disposal. In healthy people, the acids that accumulate are excreted immediately in the urine. In the case of a large excess of acid, additional auxiliary systems are used.
Among other things, our organism deposits excess acids in the form of “slags” in the connective tissue in order to mobilize and excrete them again at a later time. Only when this line of defence has been breached do the buffer systems of the aqueous solutions come into play.
A practical example:
In a healthy person, the aqueous portion of blood, urine, saliva and other body fluids is in an orderly, liquid-crystalline state. Acid metabolic products and acids from food are embedded in this structure and can thus be transported to their destination without changing the pH value of the liquid.
Studies by Professor Dr. Bernd Kröplin show that the symmetrical arrangement of the body water is disturbed in some people. In these cases, the water is no longer in liquid crystalline form, but partially in liquid form. While in a healthy person the gastric acid has a highly ordered structure, in a patient with gastric ulcer or gastritis it loses its order.
When both patients drink a glass of lemon juice, the acid contained has different effects on the organism. The chemistry of aqueous solutions applies to gastric patients, so that citric acid, as tricarboxylic acid, can give off a total of three positively charged hydrogen ions. In a healthy person, on the other hand, the stomach acid is liquid crystalline. Citric acid therefore retains its protons and enters the body unchanged, where it is metabolised in an alkaline manner. For this reason, fruit acids like citric acid belong to the base-forming foods.
What do the terms basic and acidic food mean?
When we talk about acidic and basic foods, we do not refer to the acidic term used in classical chemistry. Our understanding of acids and bases takes into account the latest findings in quantum medicine. The acid-base definition of ÁYIO-Q makes a statement about how a food behaves in the organism of a living being with its liquid crystalline state of aggregation of water and how it affects the mind.
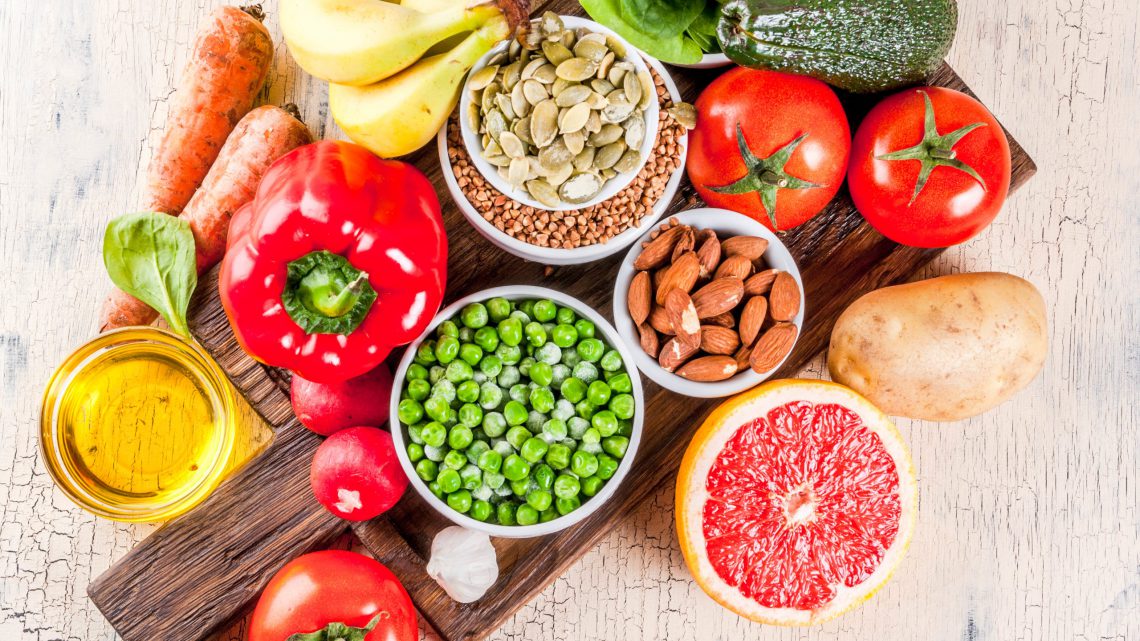
Which foods are part of an acidic diet? First and foremost are processed foods such as ready meals and sauces, refined sugar, coffee, soda drinks, alcohol, and pasta and baked goods made from white flour. But also meat and meat products (ham, sausage, offal), fish, seafood, eggs, milk, yoghurt, quark and margarine are acidic foods. The range of alkaline foods includes most fruits and vegetables, mushrooms, sprouts, herbs, apple cider vinegar and live water.
What are the effects of an alkaline and acidic diet on the body and mind?
Alkaline food contains valuable minerals such as iron, magnesium, calcium and potassium, which have an alkaline effect on our organism. The bitter substances that occur also ensure that the body itself produces basic compounds. Other advantages include:
Basic food
- is not broken down into acidic end products (slags),
- has anti-inflammatory effects due to its numerous antioxidants,
- helps build a healthy microbiome in the gut,
- has a large proportion of live water,
- contains valuable vitamins and phytochemicals which
- vitalise our body, strengthen the immune system and support the excretory organs (liver, kidneys).
Acid food, on the other hand, is rich in acid-forming amino acids and contains a large number of minerals such as fluorine, chlorine, iodine and phosphorus. These affect us in a sourly manner. In addition, acidic degradation product are produced during digestion, which promote slagging of the connective tissue.
Sour food
- is not able to stimulate base formation in the organism,
- weakens the body’s own deacidification processes,
- has only a small amount of water,
- affects the condition of our microbiome,
- promotes inflammation.
Possible symptoms of hyperacidity, which are often not recognised as such, include:
- Loss of appetite,
- Fatigue and/or tiredness,
- Nervousness and/or restlessness,
- Depressive mood,
- Cellulite (loose connective tissue)
- Muscle and/or joint problems,
- Rheumatic complaints
- Osteoporosis.
Acid-alkaline balance also plays an important role when it comes to the state of mind. People who eat an alkaline diet usually see the world around them in a much more positive light. On the other hand, those who are over-acidified are more prone to worry, anxiety and depression.3
How can a disturbed acid-base balance be brought into equilibrium?
In order to break down the acidic milieu, the most important and often the most difficult part is the consistent change in eating habits. Ideally, those affected should completely remove bread and rolls made from white flour, ready meals, fast food, industrial sugar and sugary drinks from their menu.
Those who largely avoid processed foods such as sausage products and meat from factory farming and limit their coffee and alcohol consumption create good conditions for the body’s own deacidification. What can I still eat then? Naturopaths and non-medical practitioners often hear questions like these.
The transition is about establishing a diet that is excessively alkaline. The proportion of fresh fruit, vegetables and salads should be as high as possible. Meat, fish, shrimp or mussels are of course allowed, although they increase the acid content in the body. It is important to pay attention to quality when buying. A steak or chop that is full of antibiotics and stress hormones is much less suitable than a piece of meat from an organic farmer in the vicinity.
Can our minds also help restore the acid-base balance?
In recent decades, a completely new branch of medicine has emerged: psychoneuroimmunology. She studies the influence of the human mind (psyche) on the immune system and nervous system. In particular, psychoneuroimmunology focuses on the effects of severe and prolonged stress.4
Since chronic stress shifts the acid-base balance of the body and thus makes deacidification more difficult, this aspect should also be taken into account. Relaxation techniques such as autogenic training, meditation, yoga and Jacobson’s progressive muscle relaxation help to cope better with stress.
We can influence our immune system through positive feelings so that stress-related inflammatory reactions do not occur. That is why people who are happy and satisfied and feel empathy and gratitude towards others live a healthier life. Because whoever goes through life in a grouchy and angry mood is also acidic on a physical level.
Deacidification as a naturopathic treatment approach
In addition to changing your diet, holistic therapists recommend further measures. Above all, these include:
- regular exercise
- stress relief and relaxation exercises
- breathing technique with a conscious, deep inhalation and exhalation
- alkaline fasts and alkaline baths
- drink 1.5 litres of live water daily
- if necessary, take additional basic minerals
Thanks to its naturopathic approach, the ÁYIO-Q health teaching is particularly suitable for creating a balance between body and mind. Using the physical principle of quantum entanglement, valuable subtle information is imprinted on your drinking water at home, which can help to restore the acid-base balance.
In the traditional medicine in ancient Greece, the ÁYIO-Q Center of Vitality places particular emphasis on increasing life energy and activating self-healing powers. The free self-test on the homepage provides information about your current state of life energy and self-healing powers.
Sources:
[1] Acid-Base Concepts, at https://www.chemie.de, Access date 02.05.2021
[2] Recent findings in quantum medicine confirm ancient Greek health teachings, at https://www.ayio-q.com/, Access date 02.05.2021
[3] Hyperacidity (acidosis) – causes, symptoms, treatment, at https://www.liebscher-bracht.com, Access date 02.05.2021
[4] Psychoneuroimmunology: emotions control the immune system, at https://www.pharmazeutische-zeitung.de, Access date 02.05.2021